Risk Management Chapter 4 - Contingency Planning and Management
1. Contingency planning
Aiming: To cope with some circumstances that normal operations are infeasible.
Why we need contingency plan?
- Every system is imperfect.
- There are always emergencies.
- Legal obligation.
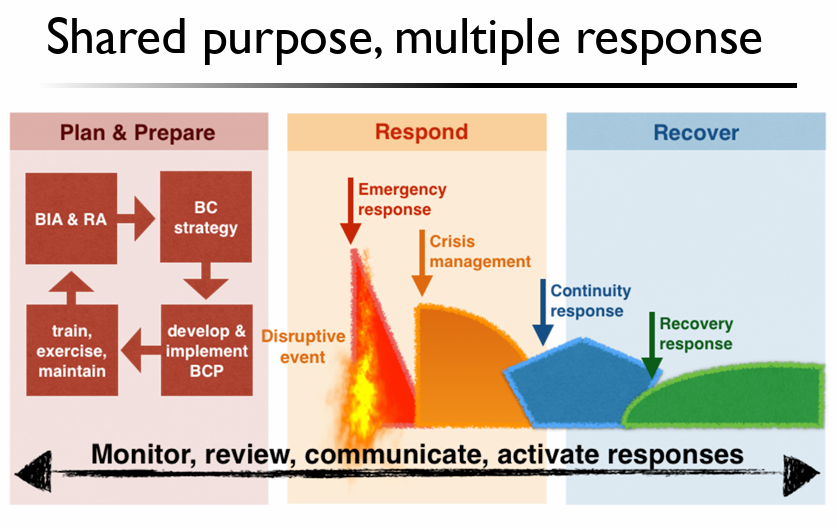
2. Multiple response paradigm
Taxnology of contingencies
Name Definition Emergency Time critical, something time critical which needs quick response to reduce damage/losses of people’s life, physical or information assets. Cirsis strategic, A situation with potential knock-on and long term adversarial effects, affecting reputation, stock prices/market, etc. Disaster Physical damage, Involves loss of physical assets and/or people’s life/health, and/or critical IT systems. Business Contiguity Management
Definition: Business Contiguity Management, namely
BCM, is broadly defined as a business process that seeks to ensure organizations are able to withstand any disruption to normal functioning.Steps:
- Emergency response
- Crisis management
- Business recovery
The life cycle of BCM
Business Continuity Planning
Process
- BIA & RA
- BC strategy fomulation
- BCP production (BCP namely is Business Continuity Planning)
- BCP testing
- BCP awareness
- Ongoing BCP maintainance
PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act)
It is an iterative four step management method used in business for the control & continuous improvement of processes and products.