Risk Management Chapter 3 - Risk Analysis and Assessment
First thing first, differences between risk, threat and vulnerabilities.
| Terminology | Definition |
|---|---|
| Vulnerabilities | Weakness of an asset or control that can be exploited by one or more threats |
| Threat | Potential cause of an unwanted incident, which may result in harm to a system or organisation |
| Risk | Effect of uncertainty on objectives |
1. Dilemmas for information security
Powerful attacking resourceVSinadequate security budget
You don’t know how much attack resources the adversaries have, so it’s hard to decide how much you should pay for security. And sometimes, there are some nation state attackers, they have way more attacking resource than you could defend.Complacency
Even if you deploy your defenses. You don’t know whether the security is brought by your defenses techniques or just because the attackers haven’t attacked you.Compliance out of compulsionThe fallacy of relative privation
You might also be attacked even you are more secure than other guys or companies.
So the conclusion is, information security shouldn’t be driven by Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt.
2. Risk Analysis
Find the assets you need to secure, maximize the protection while providing functionality.
Risk management is for different valuable assets, you need to investigate the logical and system boundary.
Multi-tier Risk Management
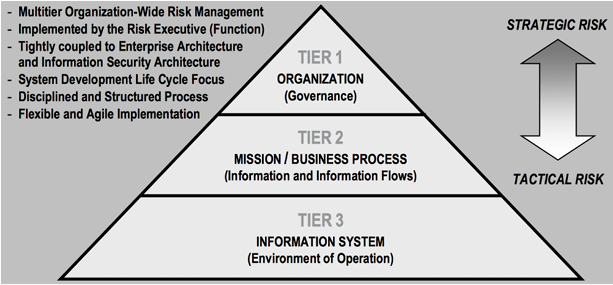
Risk Analysis Process
Information gathering
Vulnerability analysis

Categorize vulnerabilities ->
Severity&Exposure
Threat analysis
- Human Threat
- Non-Human Threat
Risk identification and analysis of acceptable risks
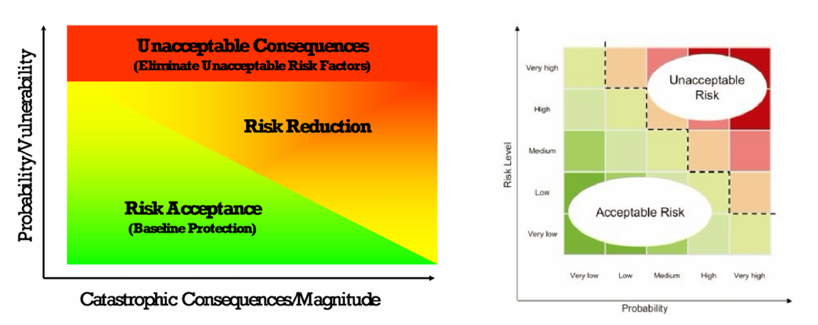
Risk Management Framework
Categorize information system
Select security controls
Implement security controls
Assess security controls
Authorize information system
Monitor security controls
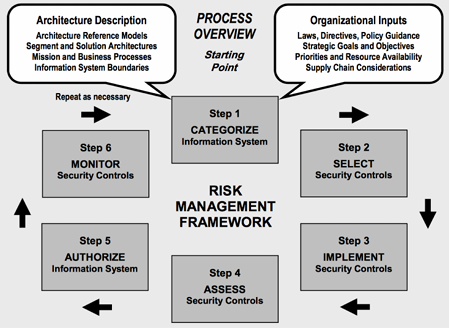
QualitativeVSQuantitativeanalysis- Quantitative is better than qualitative analysis at the most of time.
Pros Cons Qualitative - Simple to use
- Flexible
- Cover a lot of ranges
- Ambiguous
Quantitative - easy to convince
- Support budget decision
- derived from irrefutable facts
- Inapplicable(hard to generate>
- false sense of accuracy
Useful tool: Annualized Loss Expectancy -> ALE
Shortcomings of ALE:
- Cannot distinguish high-frequency, low-impact events from low frequency, high-impact events based on such a single simplified number.
- False sense of accuracy.
- Not flexible.
3. Actualize Risk Analysis
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Using a series of lower-level events to deduct the final undesired event.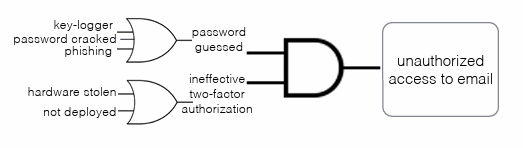
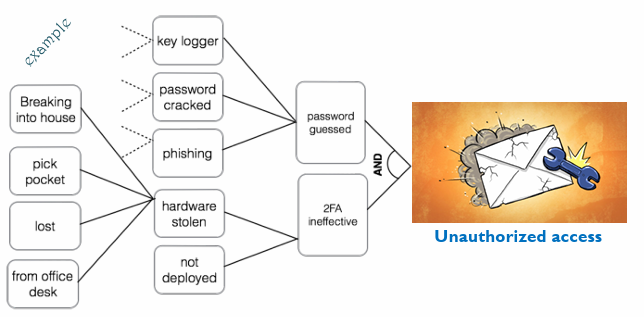
Attack Trees
Root nodes: unwanted events
Leaf nodes: attacks and the consequences
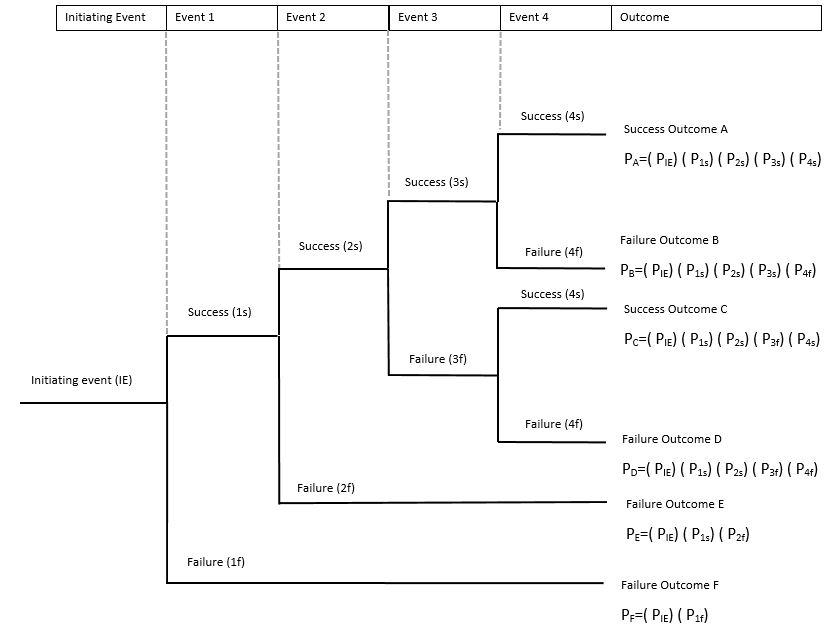
Event Tree Analysis (ETA)
Explores forward (success/failure) responses through a single initiating event. Lays a path for assessing probabilities of various outcomes.
Failure Mode & Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- probability that failure will occur.
- likelihood that failure won’t be detected.
- severity of effects of the failure.
All those three -> Risk Priority Number (RPN) = $probdetsev$
4. Conclusion
Since we don’t have infinite budget, we need to know where should we invest the money and the priorities of those places. That’s why we need Risk Analysis.
To conduct this Risk Analysis, we need to know the process of it and what tools can we use, like FTA, ETA, FMEA etc.