Risk Management Chapter 1 - Concepts and Background
1. Basic Concepts
| Terminology | Description |
|---|---|
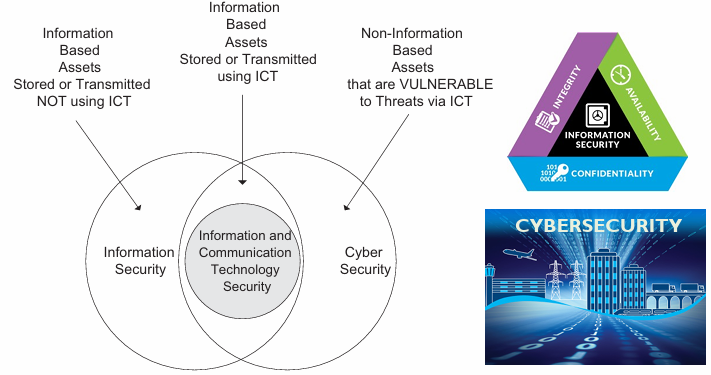
| Information Security | Security about information based assests |
| Cyber Security | Security about the transmission or communication of information |
2. Attacks & Attackers
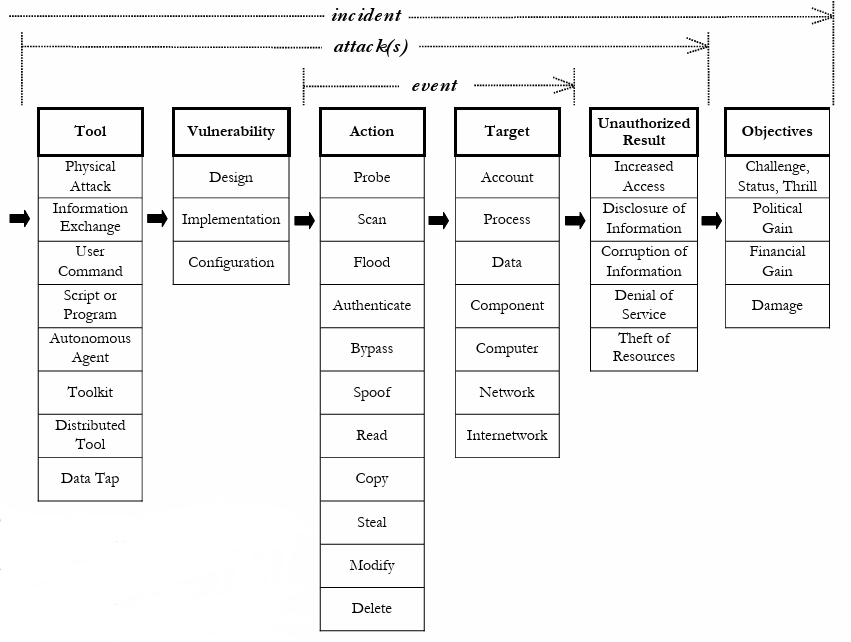
For an incident happened, we need to know:
- Tools -> ( Physical Attack/ Information Exchange/ User command/ Script or Program/ …)
- Vulnerability -> (Design/ Implementation/ Configuration)
- Action -> (Probe/ Scan/ Flood/ Authenticate/ Bypass/ Spoof/ …)
- Target -> (Account/ Process/ Data/ Component/ …)
- Unauthorized Result -> (Increased Access/ Disclosure of Information/ …)
- Objectives -> (Challenge, Status, Thrill/ Political Gain/ …)
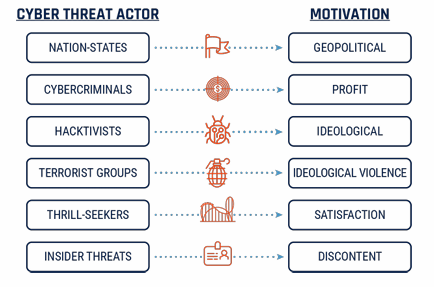
After we know how they attack, it’s easy to find their identity based on their way of attacking.
The definition of attack vector and attack surface.
| Terminology | Description |
|---|---|
| System Hardening | reduce the attack surface |
| Attack Vector | a path or means by which one can attack a system (network, server, …) exploiting the vulnerabilities of the system |
| Attack Surface | all the attack vectors in the system put together |
Trinity of Troubles - Factors leading to enlarge the attack surface.
- Extensibility: A software which could extent extral functions.
- Connectivity: There are interconnections between softwares.
- Complexity: Massive codes.
Principles of easiest penetration:
An intruder must be expected to use any available means of penetration. The penetration may not necessarily be by the most obvious means, nor is it necessarily the one against which the most solid defense has been installed. And it certainly does not have to be the way we want the attacker to behave.
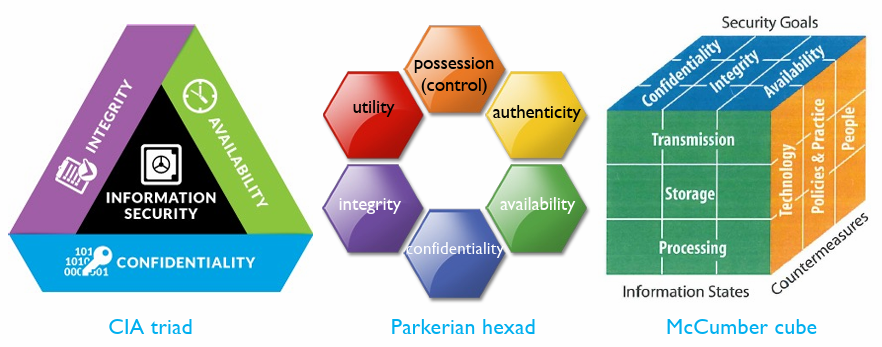
3. Secure and What to secure
Some Popular Security Models:
- CIA model: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability.
- Parkerian Hexad: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, Utility, Possessing, Authenticity.
- McCumb Cube: Security Goals(CIA), Information state(transmission, storage, processing), countermessure(Technologies, Policies&Practices, People)