Forensic Chapter 3 - Computer forensic
1. Essential Basics
Computer Forensic
Not focus on the term itself, but how to conduct it.Acuisition
Analysis
Report

Digital Evidence
Any data that is preserved in a computer system that can be read or understand by a person or computer system/applications.
Metadata vs Data
Data Volatility
File System
File System Construction FAT 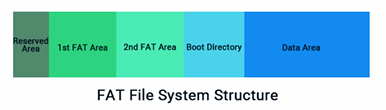
FAT32 
exFAT 
APFS 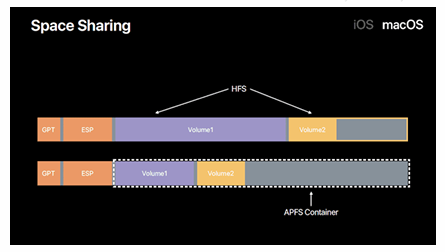
EXT 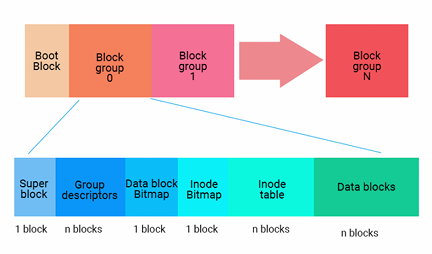
NTFS 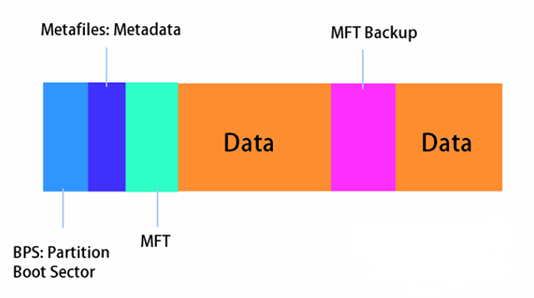
Disk Drive Anatomy
Hard Disk Drive

HDD vs Solid State Disk

SSD is tougher to restore because these is a protocol called TRIM which will force the invalid zone clear first.
2. Windows Forensic
Need to know
Important files location
Normally the important files are stored atC:\Windows\System32, files includewininit.exe,svchost.exeand so on.Auto starts registries

Hidden files
Impersonate names of legitimated files
- A:1sass.exe B:lsass.exe
- A: dllhost.exe B: dIIhost.exe
- A: EXPLORER.EXE B: EXPL0RER.EXE
Hidden by malicious users
Can use

Alternate Data Streams
Prefetch
- Maintains a list of used programs.
- Used to decrease the amount of time to open a program.
- Location:
C:\Windows\Prefetch - File Format:
filename.pf-> proprietary format - Tool to read pf file:
pecmd.exe
Signed or Not
UseSigcheck
Timeline Analysis
Corresponded Actions

Letter Connotation
M Last Modified A Last Accessed C Meta data changes B When the file was created
Windows Registry Analysis
NTUSER.DAT
Settings specific to individual users. Tracks users activity and preferences.- MUICache: Show software which has been executed on a system.
- MRU: Show software which is most recently used.
SAM
Only applicable to local or domain administrators. Contains user name, SID and encrypted password hash for all users in a domain.Security
Contains the security permissions for administrators. Used by the system to enforce security policy. Limited usefulness for forensics.Software
Contains programs and Windows settings for all software on the system.System
Contains Windows OS setup, mounted devices, hardware settings and services.