Access Control Basic
Access Control
1. Definition of Access Control
Access control is a selective restriction of access to a place of resource.
Authentication is typically the first step for access control, after successful authentication, the system decides whether the request for accessing a place/resource is granted or not based on the predefined rules/policies.
2. Access Control Model
Access control model is a scheme for specifying and
enforcing security policies. There are different classifications of access control models
According to who decides the access rights to an object:
- Discretionary Access Control -> DAC
->The owner of the object decides the rights. Example: the owner of a file decides who can read or
write the file - Mandatory Access Control -> MAC
->A policy administrator decides the policies, which must
be followed by everyone in the system. Example: NTU does not allow the students to access
the exam marks entry system
- Discretionary Access Control -> DAC
According to how to store the security policies:
- Access Control Matrix
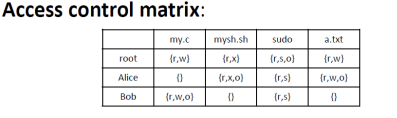
- Capability-based Model

- ACL-based Model
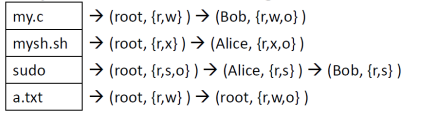
- Access Control Matrix
According to how to simplify the security policies:
- Role-based Access Control (RBAC)
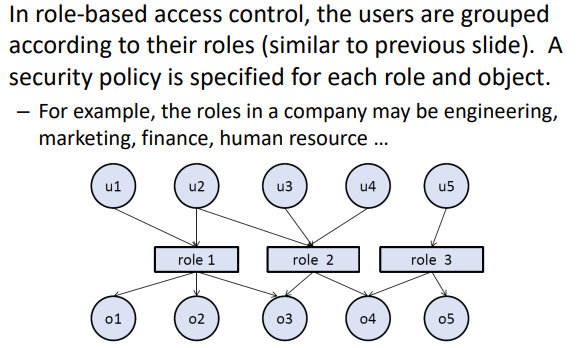
- Rule-based Access Control (RUBAC)
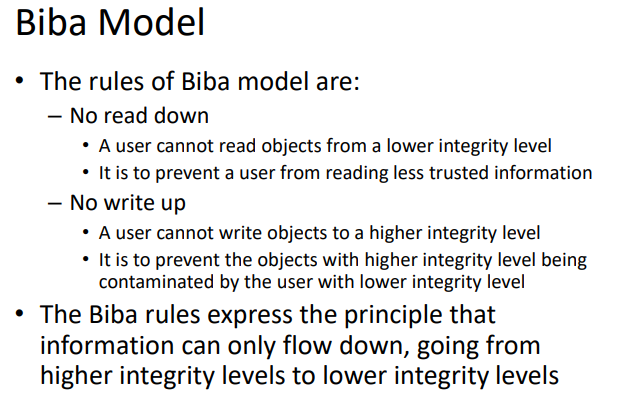
- Multi-Level Security (MLS), such as BLP model and Biba model. Multi-level security (MLS) has been traditionally used in military organizations for document classification and personnel clearance.
MLS is type of mandatory access control model. Objects are classified into different security levels. Each user is assigned a security level.
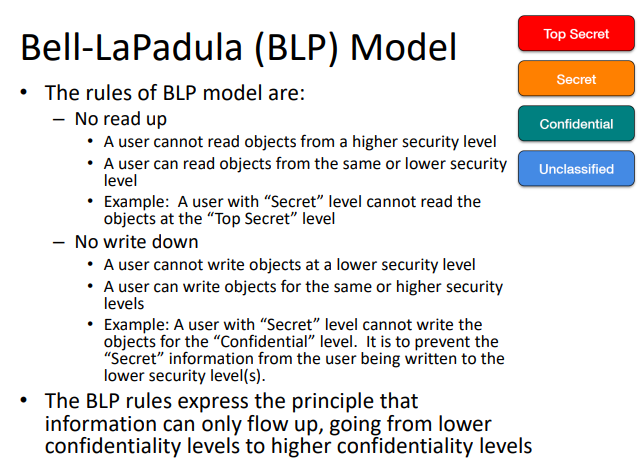
There are two main MLS models:- Bell-Lapadula model, for confidentiality.
- Role-based Access Control (RBAC)